Chain of infection transmission nursing-Definition,example of chain of infection and six different links of Chain of infection transmission is infectious agent, reservoir, portal of exit, means of transmission, portal of entry. and the new host (Susceptible host )
Definition: The Chain of Infection transmission
Infectious disease results from the interaction of an agent, a host, and an environment. Most of Infectious diseases follow a typical chain of infection that ends with an infected host. Understanding the chain of infection transmission can help with both the prevention of infection transmission and treatment of infectious diseases.
How do viruses pass from one person to the next? example of Chain of Infection transmission – When one child has a cold or flu at school, why is the rest of the class likely to come down with one next week? this happened due to Chain of Infection transmission . Let’s know more about how infection gets from one place to another, or the chain of infection transmission.
Chain of infection transmission in order
The chain of infection, is made up of six different links infectious agent, reservoir, portal of exit, means of transmission, portal of entry. and the new host (Susceptible host ). Each link has a unique role in the chain of Infection transmission, and each can be interrupted, or broken, through various means.
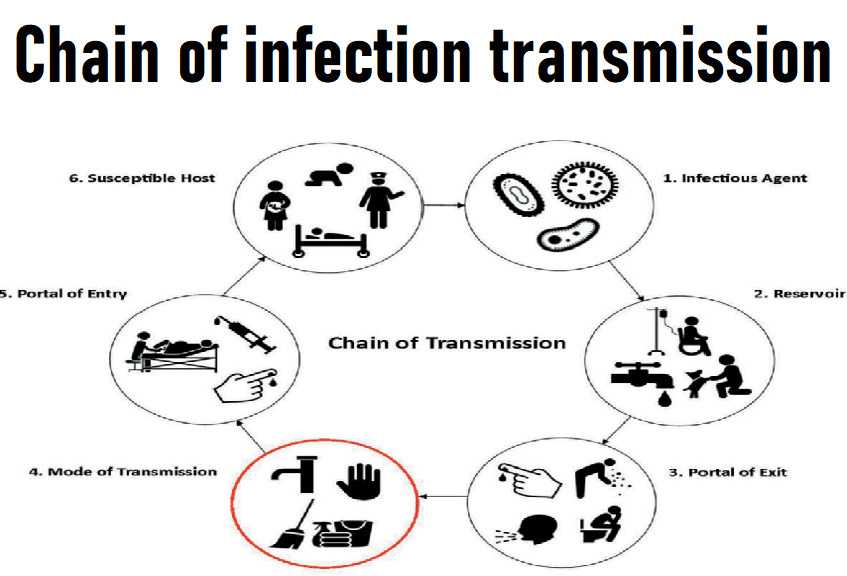
Infectious agents
Organisms that can cause an infection or an infectious disease are known as infectious agents. They include parasites, viruses, fungi, bacteria, and fungi.
Reservoir
The environment where an infectious agent typically lives, develops, and reproduces is known as the reservoir. Reservoirs include humans, animals, and also the environment. The reservoir may or may not be the source from which an infectious agent is transferred to a host.
Portal of exit
Portal of exit is the path by which a infectious agent leaves its host. The portal of exit usually corresponds to the site where the infectious agent is localized.
Example of Portal of exit
some Example of Portal of exit is
- Influenza viruses and Mycobacterium tuberculosis exit the respiratory tract
- schistosomes through urine
- cholera vibrios in feces
- Sarcoptes scabiei in scabies skin lesions
Modes of transmission
An infectious agent may be transmitted from its natural reservoir to a susceptible host in many different ways. There are different classifications for modes of transmission. Here is two classifications of mode of transmission:
Direct Modes of transmission
In direct transmission, an infectious agent is transferred from a reservoir to a susceptible host by direct contact or droplet spread.some Example of Direct Modes of transmission is
- Direct contact
- Droplet spread
Indirect Modes of transmission
Indirect Modes of transmission involves coming into contact with a contaminated object. This frequently happens as a result of dirty hands contaminated objects or environments.some Example of Indirect Modes of transmission is
- Airborne
- Vehicleborne
- Vectorborne
Portal of entry
The portal of entry refers to the manner in which a infectious agent enters a susceptible host. The portal of entry must provide access to tissues in which the infectious agent can multiply or a toxin can act. Often, pathogen use the same portal to enter a new host that they used to exit the source host.
Example of Portal of entry
Influenza virus exits the respiratory tract of the source host and enters the respiratory tract of the new host.
Host
The final link in the chain of infection is a susceptible host. Susceptibility of a host depends on genetic and immunity, and nonspecific factors that affect an individual’s ability to resist infection or to limit pathogenicity. An individual’s genetic makeup may either also increase or decrease susceptibility
