foetal skull its diameters Sutures and Fontanelle -The fetal skull comprises of:
– Vault, and
– Base
Bones of fetal head are compressible, along these lines encourage in simple conveyance while head going through the birth section in second phase of conveyance.
Landmarks of Foetal Skull
- Occiput
- Sinciput – is the temple
- Parietal eminences – are eminences of parietal bones on either side
- Mentum is the jawline
- Vertical point is the focal point of sagittal suture
- Frontal point is the foundation of the nose is called glabella
- Subocciput is the intersection of fetal neck and occiput (scruff of neck)
- Submentum is the intersection among neck and jawline
- Biparietal is the transverse separation between two parietal eminences
- Bitemporal is the separation between two lower parts of the bargains.
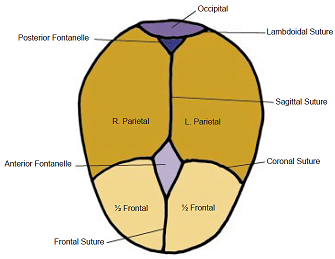
foetal skull its diameters Sutures and Fontanelle -fetal skull Sutures and Fontanelles
Sutures– Sutures are intersections of edges of at least two bones. Fontanelles are membraneous space shaped by unossified film isolating edges of bones of fetal skull.
There are four significant sutures on fetal skull:
- – Sagittal suture
- – Frontal suture
- – Coronal suture
- – Lambdoidal suture
Fetal head indicating sutures and fontanelle
Fontanelles
Anterior Fontanelle or Bregma: It is jewel molded of unossified film. It is the intersection of frontal, coronal (left and right) and sagittal sutures. It hardens following year and a half after birth.
Posterior Fontanelle or Lambda: It is triangular suture line at intersection of sagittal and lambdoidal suture.
Clinical Importance of Sutures and Fontanelle
1) Palpation of sagittal suture with fontanelle in labor can distinguish Vertex Presentation. Position of fontanelles and sagittal suture can recognize demeanor and position of vertex.
2) Overlapping of cranial bones at sutures implies trim of fetal head.
Locales of Fetal Skull
– Vertex
– Face
– Brow
Diameter of Foetal Skull
Suboccipito bregmatic 9.5 cm Vertex (completely flexed)
Suboccipito frontal 10 cm Vertex (deflexed head)
Occipito frontal 11.4 cm Vertex (outrageous augmentation)
Submentobregmatic 9.5 cm Face totally broadened
Submento vertical 11.5 cm Incomplete broadened face in face introduction
Mento vertical 13.5 cm Brow introduction
Bitemporal 8.2 cm
Biparietal 9.5 cm
Changes in Fetal Skull During Labor
Moulding : It is the modification fit as a fiddle in fetal head because of covering of cranial bones at sutures. In ordinary work, forming is physiological and innocuous. It vanishes inside hardly any hours after conveyance. Extraordinary trim in cephalopelvic disparity is obsessive and causes intracranial worry after birth.
Caput succedaneum : It is confined area of oedema on feotal skull on vertex introduction because of weight impact of expanding vaginal introitus and cervical ring. It typically creates after burst of layer. Caput likewise frames on face and forehead however not in breech introduction. Caput succedaneum is physiological and vanishes in 24 hours after birth of infant.
