In this article Types of Hospital Waste, risk waste groups,Non-Risk Waste, Hospital Waste Management, Risk From Hospital Waste types of hospital waste in the nursing foundation
Types of Hospital Waste
Healthcare (Hospital) waste includes all the waste generated by healthcare establishments, research facilities, and laboratories. Hospital waste includes potentially harmful microorganisms that have the potential to be hazardous and can infect hospital patients, healthcare professionals, and members of the public. Hospital waste is the second most hazardous waste after radioactive waste. The improper management of hospital wastes causes serious environmental problems in terms of air, water, and land pollution
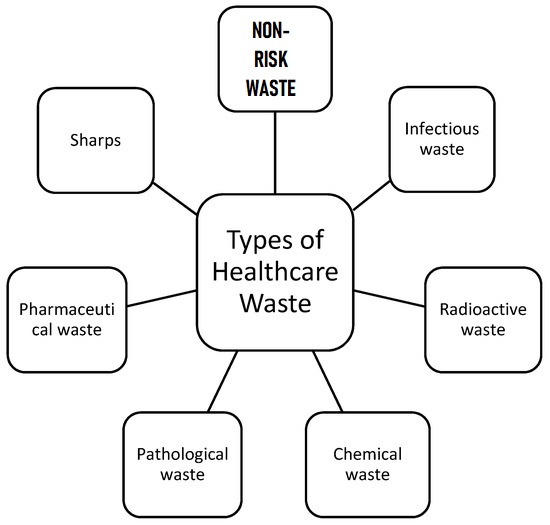
Types of Hospital Waste is divided into Risk Waste and Non-Risk Waste.
Risk Waste
Hospital wastes are categorized according to their weight, density, and constituents. The World Health Organization (WHO) has classified medical waste into different categories. Types of Hospital Waste i.e. Risk waste are also divided into seven groups.
- Infectious waste
- Pathological waste
- Sharps
- Pharmaceutical waste
- Genotoxic waste
- Chemical waste
- Radioactive waste
- Sharps: disposable needles, syringes, infusion sets, saws, blades, broken glasses, nails or any other item that could cause a cut;
Types of Hospital Risk Waste
list the types of hospital risk waste is:
Infectious Waste
Infectious material-containing pathogens in sufficient concentrations or quantities that, if exposed, can cause diseases e.g. laboratory cultures, waste from isolation wards, tissues (swabs), materials, or equipment that have been in contact with infected patients’ excreta.
Pathological Waste
Pathological waste includes tissues, organs, body parts, human flesh, fetuses, blood and body fluids.
Sharps
Sharps include:disposable needles, syringes, infusion sets, saws, blades, broken glasses, nails or any other item that could cause a cut
Pharmaceutical Waste
Pharmaceuticals waste containing drugs and chemicals that are returned from wards, spilled, outdated, contaminated, or are no longer required (bottles, boxes, gloves, masks, tubes)
Genotoxic Waste
Genotoxic waste-containing substances with genotoxic properties e.g. waste containing cytostatic drugs (often used in cancer therapy), and genotoxic chemicals.
Chemical Waste
Chemical waste containing chemical substances. Chemical waste can include the following:
- laboratory reagents
- film developer
- disinfectants that are expired or no longer needed
- solvents
- Cadmium waste, mainly from discarded batteries.
Radioactive Waste
These wastes include Liquid, solid, or gaseous waste. Radioactive waste contaminated with radioactive substances is used in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases. Some examples of Radioactive hospital Waste
- unused liquids from radiotherapy or laboratory research
- contaminated glassware, packages
- absorbent paper
Non-Risk Hospital Waste
Non-risk Hospital waste is that, creates no greater risk than waste from a typical home and is comparable to normal domestic garbage. Almost everyone in the hospital produces this typical trash, I.e., administration, patient risk, cafeterias rooms, and nursing station. Non-Risk Hospital Waste includes:
- Paper
- cardboard.
- Food waste
Hospital Waste Management
Hospital Waste Management means the supervision of waste produced by hospitals using techniques that will help to check the spread of diseases through it. The management of Hospital waste poses to be a major problem in most countries, especially hospital waste. It is an ongoing problem for many countries. In recent years, medical waste disposal has posed even more difficulties with the appearance of disposable needles, syringes, and other similar items.
Single-use or disposable, healthcare products help hospitals avoid the environmental problems with laundry and sterilizing operations associated with traditional products, which consume chemical and energy resources and emit wastewater and greenhouse gases.
Risk From Hospital Waste
Everyone who comes into contact with hazardous biological waste or is exposed to it as a result of poor management is possibly at risk. This includes anyone who handles the material at any point. An extensive range of pathogenic microorganisms may be present in the infectious waste. These pathogens in the waste can enter the body of a living thing in a number of ways, such as through a wound in the skin, through the mucous membrane, by inhalation, or through ingestion.
